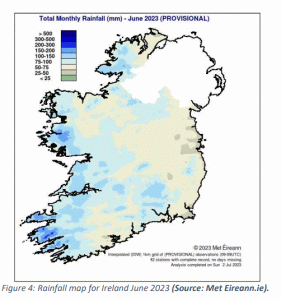
The hydrology bulletin is based on rainfall, river flows, lake levels, groundwater levels and spring outflows at monitored sites for the month of June. Rainfall for June was generally below the long-term average in most places across the country.
The monthly average river flows for June reflect this and fell at almost all river monitoring since May and were below the long-term average for this month. Almost two-thirds (65%) of river stations were below the normal range for June. Similarly, 58% of lake and turlough stations observed flows below the normal range for this month.
Average monthly groundwater levels for May also fell at 97% of monitoring wells with more than half (57%) of monitoring wells observing levels below the long-term average for June. Similarly, most monitored spring outflows were in the normal range or below average for this time of year.
Lower river flow levels, coupled with the warm temperatures recorded this June will result in warmer water temperature. Warm water holds less oxygen and this can have a detrimental impact on fish and other aquatic species. Maintaining riparian vegetation is essential to provide shade that will help maintain cooler water temperatures. It also provides habitats for biodiversity, absorbs greenhouse gases, traps and uses nutrients that might otherwise pollute the water.
The Water Forum have made a submission to the Climate Change Advisory Council requesting that they take a catchment-based approach to climate action planning that will identify the co-benefits for water quality and biodiversity of actions for climate adaptation and mitigation.
Water Forum Submission to the Climate Change Advisory Council
EPA Hydrology Bulletin
Monitoring & Assessment: Freshwater & Marine Publications | Environmental Protection Agency (epa.ie)